Forecasts used to be a guessing game. People relied on cloud shapes, aching joints, or old farmer’s tales to predict the weather. Sometimes they were right but mostly, they weren’t.
Today, forecasts are sharper, faster, and more detailed than ever. You can check your phone and plan your day down to the hour. So how did we get here? Let’s break it down.
1. Supercomputers

Weather models use some of the world’s most powerful supercomputers, performing billions of calculations every second to simulate air, moisture, and pressure movement. This computational power allows meteorologists to run multiple forecasts, compare results, and refine predictions, leading to more accurate forecasts with less guesswork.
2. Better Weather Models
Weather models are like complex math puzzles predicting the atmosphere’s next moves, and today’s models are more advanced than ever. They account for factors like ocean currents, snow cover, soil moisture, and even wildfire smoke, leading to more accurate forecasts as scientists continue to improve them.
3. Satellite Technology

Modern satellites orbit Earth, capturing real-time images of the atmosphere to track storms, measure cloud heights, and monitor temperature and humidity. These observations are fed directly into weather models, allowing meteorologists to spot potential issues early and adjust forecasts with up-to-date information.
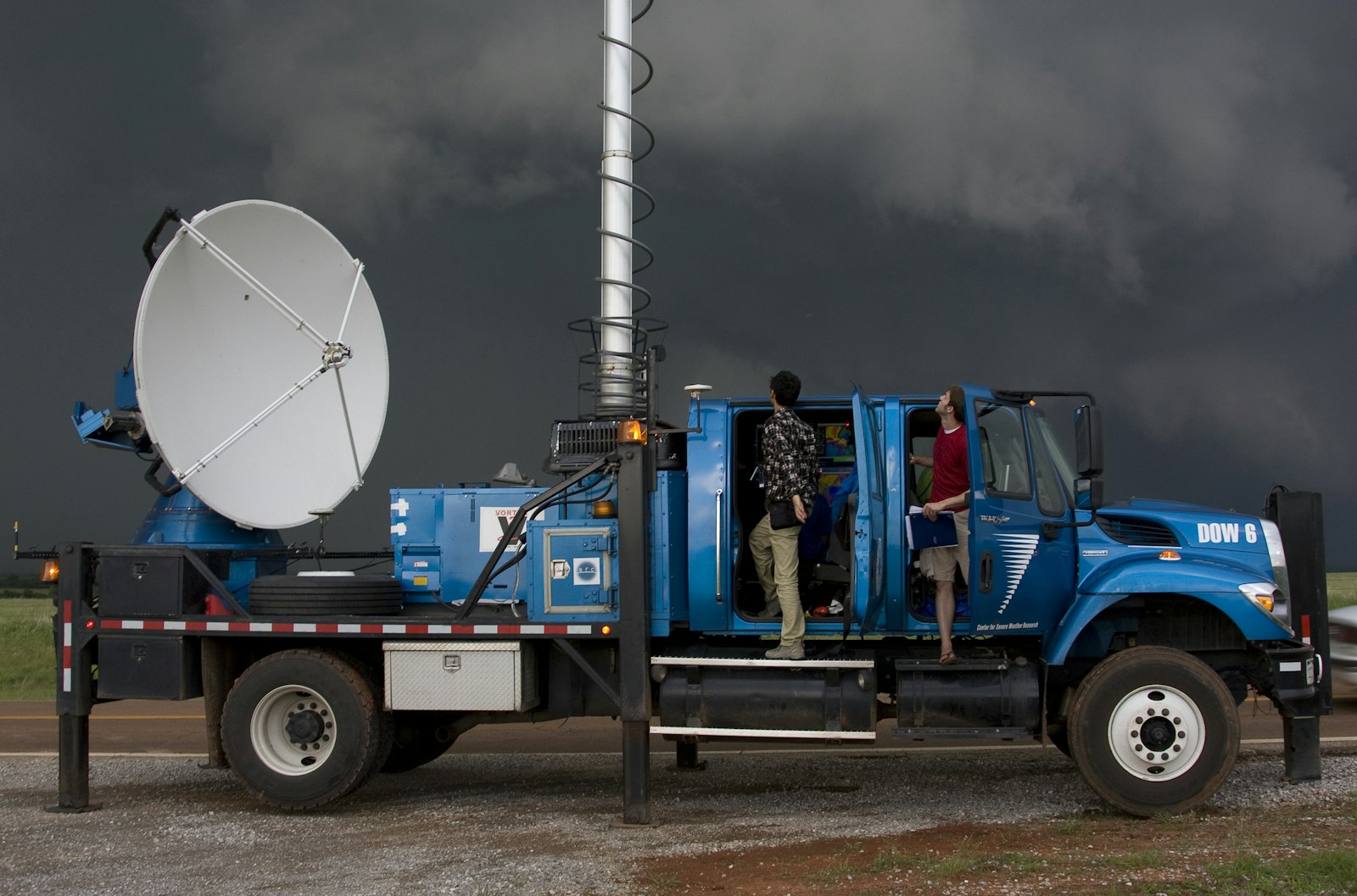
4. Doppler Radar

Doppler radar tracks rain, hail, snow, and wind patterns within storms, helping meteorologists detect tornado rotation before it touches down. This radar data allows forecasters to pinpoint the storm’s path, strength, and affected areas sometimes down to the neighborhood level.
5. Crowdsourced Data

Smartphones, cars, and even backyard weather stations now contribute real-time data on temperature, pressure, and wind, adding millions of reports daily. This vast network helps fill in gaps between official stations, allowing forecasters to create hyper-local forecasts tailored to specific communities.
6. Improved Observation Networks
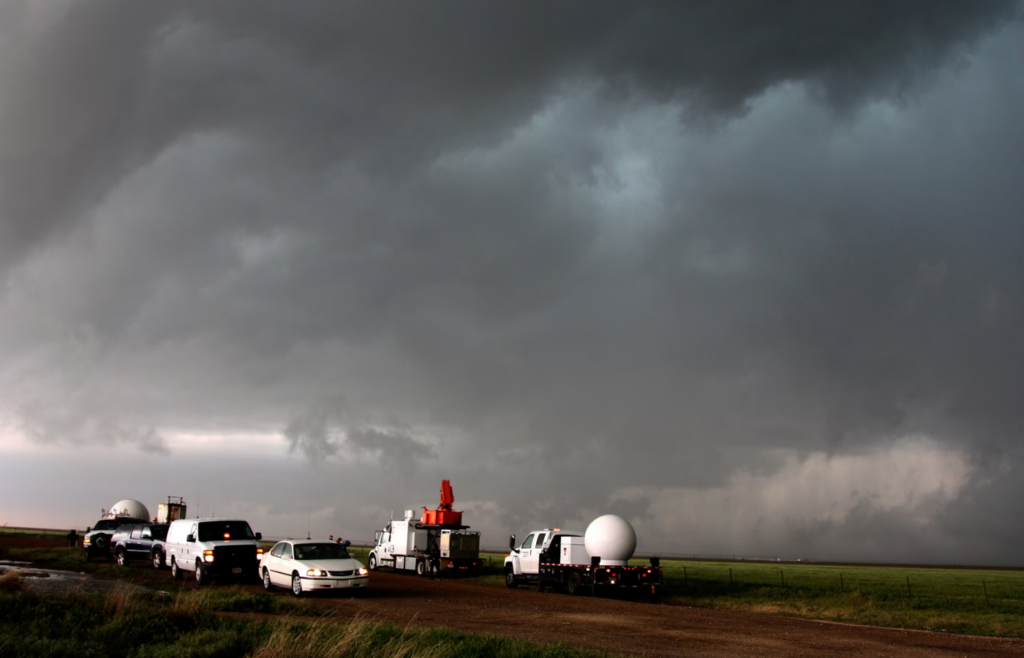

From ocean buoys to mountaintop sensors, modern observation tools track everything from soil temperature to sea-level pressure, covering more of the Earth than ever before. The more data scientists collect, the clearer the overall picture becomes, improving forecast accuracy not just locally, but globally.
7. Faster Communication

When forecasts change, speed is crucial. With push alerts, social media, and 24/7 weather channels, updates reach the public almost instantly, ensuring you get the latest warnings before a storm hits, not hours later.
8. Ensemble Forecasting

Instead of relying on a single prediction, forecasters run multiple simulations with slight variations, known as ensemble forecasting, to explore the full range of possible outcomes. This method increases forecast confidence and helps meteorologists communicate uncertainty if ten models agree, they’re more likely to be right.
Read More: 15 Smartest Ways to Prepare for a Hurricane Before It Hits
9. Machine Learning and AI

Artificial intelligence is helping meteorologists detect patterns that might be missed by humans, analyzing years of data to identify trends and refine models. While AI isn’t replacing experts, it’s becoming a valuable tool for improving both short-term and long-range forecasts.
Read More: Never Do These 10 Things During a Thunderstorm
10. Human Expertise

Even with all the technology, forecasting still depends on skilled meteorologists who interpret data, weigh models, and use real-world experience. A good forecaster knows when to trust the model and when to question it, adding a layer of human insight that enhances accuracy beyond what software alone can provide.
Thanks to science, teamwork, and technology, today’s forecasts are more than just educated guesses. They’re roadmaps for your day and sometimes, lifesavers in a storm.
Read More: Top 10 Weather Phenomena That Science Still Doesn’t Fully Understand





